Have you ever wished your smart home devices could work faster, respond instantly, and keep your personal data safer? That’s exactly where edge computing comes in.
It’s not just a tech buzzword—it’s a game-changer for the way your smart home systems operate. Imagine your smart thermostat, security cameras, or voice assistants making decisions locally, without relying on faraway servers. This means quicker responses, fewer glitches, and greater privacy for you and your family.
In this blog, we’ll break down what edge computing is, how it transforms smart home technology, and why it could be the key to a smoother, smarter living experience. Keep reading—you won’t want to miss how this innovation can make your home feel even more connected and secure.
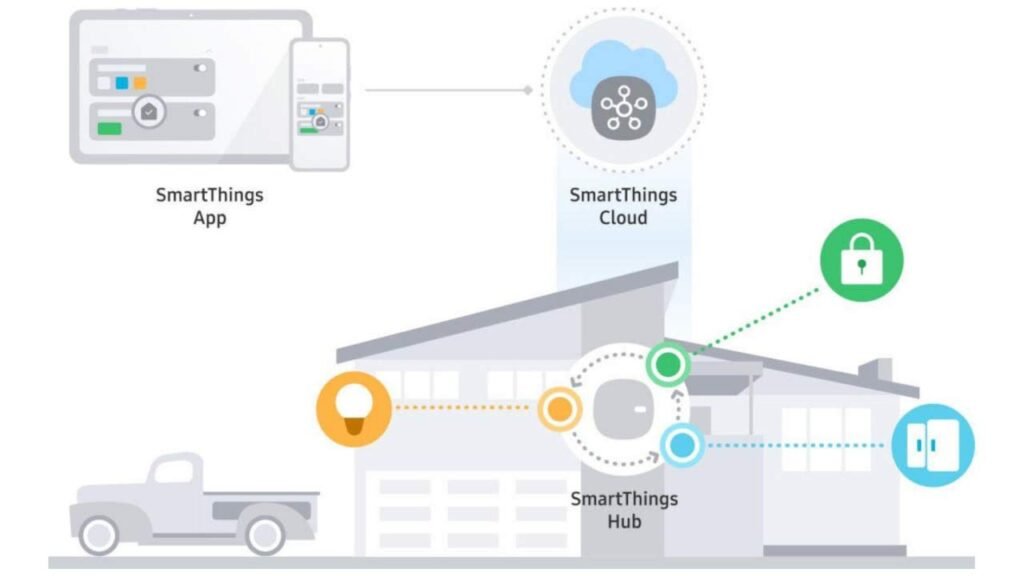
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Edge Computing In Smart Homes
Have you ever wondered how your smart home devices respond so quickly to your commands? The answer lies in edge computing. Instead of sending all data to a central cloud server, edge computing processes the data locally—right on the device or near your home network.
This approach reduces delays, keeps more of your personal data private, and ensures your smart home runs smoothly even if your internet connection is spotty. Let’s dive into how edge computing transforms your smart home experience.
1. Faster Response Times
Imagine asking your smart speaker to turn on the lights. With edge computing, the device doesn’t need to send your request to a server miles away. Instead, it processes the command locally.
This means your lights respond almost instantly. No more waiting or dealing with frustrating delays just because your internet speed isn’t cooperating. It’s all about making your smart home feel seamless and responsive.
2. Increased Privacy
Do you ever worry about where your smart home data goes? Edge computing keeps most of it local, reducing the amount of information sent to the cloud. This lowers the risk of your data being intercepted or misused.
For example, a smart camera with edge computing can analyze video feeds and only send alerts when something unusual happens. Your private moments stay private, which gives you peace of mind.
3. Reliable Performance Without Internet
What happens to your smart home during an internet outage? With edge computing, many devices can keep functioning even without a connection. A thermostat can still adjust the temperature, and motion sensors can still secure your home.
This ensures your home remains smart and functional, even when the Wi-Fi decides to take a break. It’s one less thing to stress about during downtime.
4. Energy Efficiency
Smart devices with edge computing are often more energy-efficient. By processing data locally, they reduce the energy used to send and receive information from the cloud. This not only saves energy but can also prolong the battery life of devices like smart doorbells or cameras.
Plus, less reliance on cloud servers means reduced energy consumption on a broader scale. It’s a win-win for you and the planet.
5. Is Edge Computing Right For Your Smart Home?
Think about your current smart home setup. Do you value fast responses, data privacy, and reliable performance? If yes, then edge computing could be a game-changer for your home system.
Look for devices that mention edge processing capabilities when shopping for smart gadgets. You’ll notice the difference in how your home operates—faster, smarter, and more secure.
What features do you prioritize in your smart home? Let us know in the comments below!

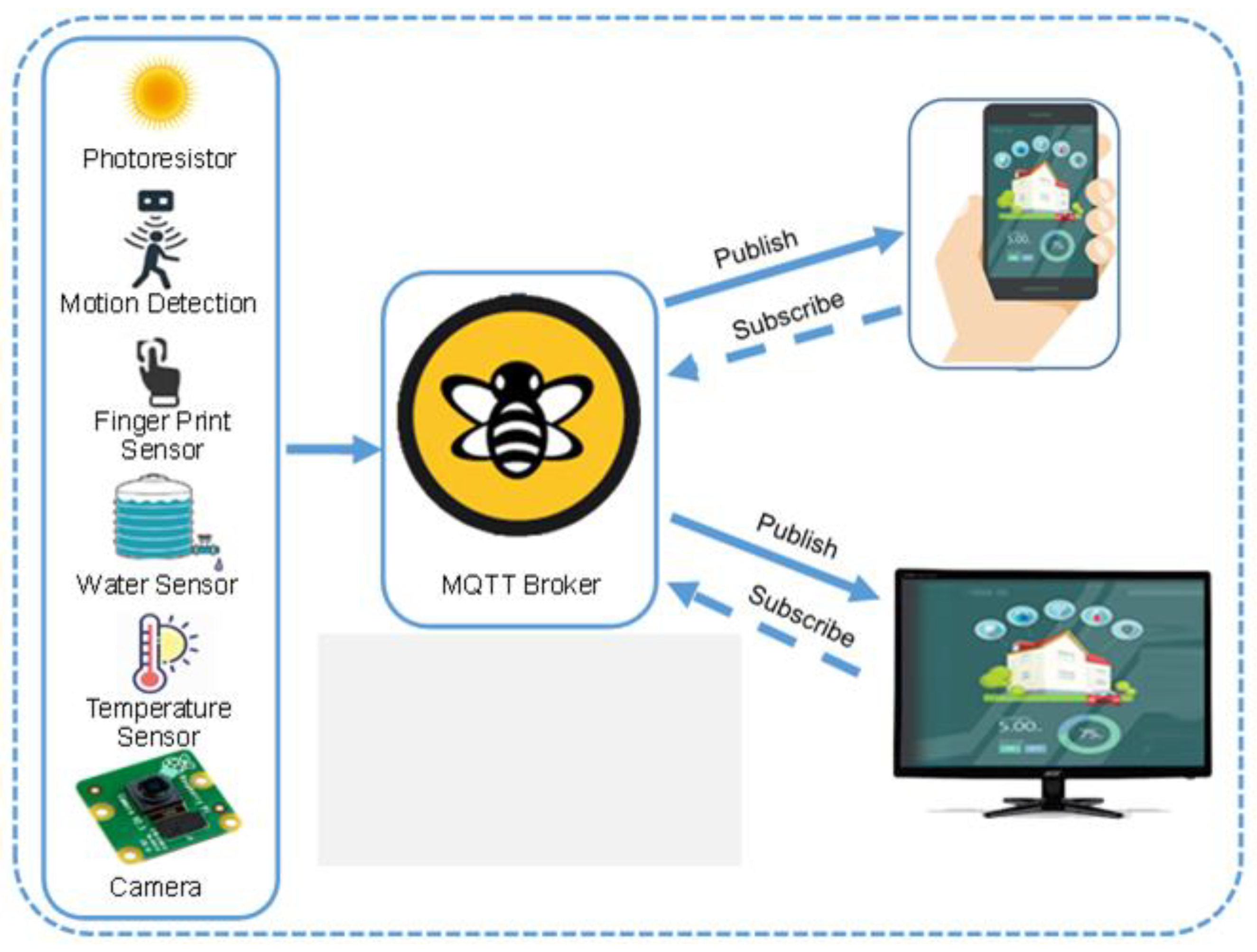
Credit: www.dreamstime.com
How Edge Computing Works
Edge computing is transforming smart home systems by processing data closer to where it is generated, rather than relying on distant cloud servers. This approach enhances speed, security, and reliability. But how does it actually work in your smart home?
How Data Is Processed Locally
Edge computing works by handling data locally on devices within your home. For instance, your smart thermostat analyzes temperature changes and adjusts settings right on the device, without needing to send that data to the cloud.
This local processing reduces delays because the data doesn’t travel far. You get faster responses, like lights turning on instantly when motion is detected.
Role Of Edge Devices
Devices like smart cameras, thermostats, and speakers act as “mini computers” in edge computing. They process and store data using built-in hardware and software.
Imagine your smart security camera identifying movement and alerting you. It does this using its internal processing power, saving time compared to waiting for cloud-based analysis.
Communication Between Devices
Edge computing allows smart devices in your home to communicate directly with each other. Your smart doorbell can notify your smart lights to turn on when someone approaches.
This creates a seamless experience, making your home feel truly connected. It also reduces reliance on external servers, ensuring operations continue even during internet outages.
Why It’s Better For Privacy
Edge computing minimizes the amount of personal data sent to the cloud. For example, voice commands to your smart assistant are processed locally, keeping sensitive information within your home.
This not only speeds things up but also gives you more control over your data. You don’t have to worry as much about external breaches.
Edge computing brings intelligence right into your home, making smart devices faster, safer, and more reliable. Have you ever wondered what your smart home could do if it were smarter? Edge computing might be the answer you’re looking for.
Key Benefits For Smart Homes
Edge computing is shaping the future of smart homes by offering faster, more secure, and reliable operations. It processes data locally on devices rather than relying solely on cloud servers. Let’s break down why this is a game-changer for your smart home with these key benefits.
Reduced Latency
Ever asked your smart speaker to turn on the lights and waited too long for it to respond? That delay, or latency, happens when data has to travel to a distant cloud server and back. With edge computing, your devices process data locally, ensuring quicker responses.
This near-instant reaction time is crucial for tasks like unlocking your smart door or adjusting your thermostat. Imagine your smart security camera detecting motion and notifying you within seconds—edge computing makes that possible.
Enhanced Data Privacy
Do you ever feel uneasy about your personal data being stored on cloud servers far away? Edge computing reduces that risk by processing sensitive information locally. This means your data stays within your home network rather than being sent to external servers.
Take your smart doorbell, for example. With edge computing, video footage can be analyzed and stored locally, limiting exposure to potential cyber threats. You gain more control over who has access to your data.
Improved Reliability
What happens to your smart home when your internet goes down? Without edge computing, your devices may stop working properly. But with local data processing, many functions can continue to operate even without an internet connection.
Your smart lights can still follow schedules, and your security cameras can keep recording. This reliability ensures your smart home remains functional when you need it most.
Which of these benefits appeals most to you? Whether it’s faster responses, better security, or uninterrupted service, edge computing is redefining how smart homes work for us.
Applications In Smart Home Devices
Edge computing enhances smart home systems by processing data locally on devices. It reduces latency and improves efficiency. This approach supports real-time responses for security cameras, voice assistants, and automated appliances, ensuring seamless operation without relying heavily on cloud servers.
Edge computing is transforming how smart home devices operate. It enables faster data processing and response times. By processing data locally, it reduces reliance on cloud servers. This enhances privacy, reliability, and device efficiency. Below are some key applications in smart home systems.Smart Lighting Systems
Edge computing makes smart lighting systems more responsive. Sensors and controllers process data directly on-site. Lights adjust instantly based on user preferences or environmental changes. For example, lights can dim or brighten based on room occupancy. This improves energy efficiency and user comfort.Voice Assistants And Ai
Voice assistants use edge computing to process voice commands locally. This reduces delays and ensures quicker responses. For example, devices like smart speakers can adjust volume or play music instantly. It also enhances privacy by limiting data sent to cloud servers. AI-powered devices learn user habits faster with local processing.Home Security And Surveillance
Edge computing improves home security by processing video feeds locally. Cameras can detect motion or unusual activity in real time. Alerts are sent immediately without relying on cloud processing. This ensures faster responses during emergencies. It also keeps sensitive footage within the home network, enhancing security. “`Role In Energy Efficiency
Smart home systems are transforming the way we manage energy use. Edge computing plays a pivotal role in making these systems more efficient. By processing data locally, it allows real-time adjustments that reduce waste and save energy.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing processes data closer to where it’s generated, right on your devices or within your home network. Unlike cloud computing, it doesn’t rely on sending data to distant servers. This localized approach enables quick responses and reduces delays.
How Does Edge Computing Optimize Energy Use?
Imagine your smart thermostat adjusting heating or cooling based on your daily routine. Edge computing analyzes patterns locally and makes instant decisions. It avoids unnecessary energy use and keeps your home comfortable without overworking appliances.
Real-time Monitoring And Adjustment
Edge computing enables real-time monitoring of your energy consumption. Smart plugs, lighting systems, and thermostats can respond to live data. If your living room is empty, lights can turn off without waiting for cloud-based instructions.
Reducing Dependency On Cloud Services
Cloud computing can introduce delays and use more energy for data transmission. Edge computing eliminates this dependency. It processes data locally, reducing energy spent on communication and cutting down your electricity bill.
Practical Benefits For You
- Lower electricity bills as devices use energy only when necessary.
- Faster response times for smart home systems to adapt to your needs.
- Greater reliability, especially during internet outages.
Is Edge Computing The Future Of Energy Efficiency?
Think about how much energy could be saved with smarter systems. Edge computing makes smart homes not only intelligent but also sustainable. Would you prefer a home that anticipates your energy needs or one that wastes power while waiting for a command? The choice is yours.

Credit: site.nyit.edu
Challenges And Limitations
Edge computing is transforming smart home systems by enabling faster processing, improved security, and reduced reliance on centralized cloud servers. However, it’s not without its challenges and limitations. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions when integrating edge computing into your home.
Hardware Costs
Edge computing requires specialized devices with processing power, storage, and connectivity capabilities. These devices are often more expensive than standard smart home gadgets. For example, installing an edge-enabled hub or camera can cost significantly more than a basic alternative.
Upgrading all your smart devices to support edge computing may not be financially feasible for everyone. It’s worth prioritizing critical devices, like security systems, before expanding further. Would you pay more upfront for better performance and privacy?
Integration Complexities
Smart home systems often involve devices from different brands and ecosystems. Getting them all to work seamlessly with edge computing can be a headache. Compatibility issues can arise, especially if older devices lack the necessary software or hardware support.
Even with newer devices, you may encounter challenges in syncing data and ensuring smooth communication. Consider whether your current setup can handle edge computing before diving in. Are you ready to troubleshoot or invest in professional setup services?
Scalability Issues
Edge computing solutions are often tailored for specific tasks or devices. Adding more devices to your smart home system can strain the edge network. For instance, a smart thermostat or camera might work flawlessly at first, but adding more devices could lead to slower processing or connectivity issues.
If you plan to expand your smart home over time, scalability should be a key consideration. Can your edge computing setup grow with your needs? Thinking ahead can save you time and frustration down the road.
Future Of Edge Computing In Smart Homes
As technology evolves, edge computing is shaping the future of smart homes. It’s not just about controlling lights or adjusting the thermostat anymore. Edge computing promises smarter, faster, and more secure home automation by processing data locally on devices, rather than relying on cloud services. But what does the future really look like for edge computing in your home?
How Edge Computing Can Make Your Smart Home Faster
Imagine your smart home reacting instantly to your commands without delay. Edge computing allows devices like smart cameras or voice assistants to process data locally instead of sending it to the cloud. This reduces lag, making your home automation feel seamless.
Think of a smart doorbell recognizing a visitor at your door in real-time. No waiting for cloud servers to analyze the video feed—your home responds immediately. Faster responses mean better user experience and fewer frustrations.
Boosting Privacy With Edge Computing
Are you concerned about data privacy? Edge computing addresses this by keeping sensitive data within your home network. Personal information doesn’t need to travel to external servers, reducing risks of breaches.
Your security cameras, for instance, can process footage locally. This ensures that private moments remain private, giving you peace of mind. You control what data leaves your home.
Energy Efficiency In Smart Homes
Smart homes powered by edge computing can optimize energy usage. Edge devices can analyze patterns and adjust settings without relying on cloud-based algorithms. This saves electricity and reduces your bills.
For example, a smart thermostat can learn your habits locally and adjust heating or cooling based on your schedule. It’s efficient and sustainable, helping you contribute to a greener future.
Challenges Ahead For Edge Computing In Homes
While edge computing offers exciting possibilities, it’s not without challenges. Devices need more powerful hardware to handle local processing. This can increase costs upfront.
Compatibility between different smart devices can also be tricky. Will your smart fridge communicate smoothly with your edge-powered energy monitor? These are hurdles that developers and manufacturers need to solve.
What Role Will You Play In This Future?
The future of edge computing isn’t just about technology—it’s about you. How will you embrace these advancements? Will you prioritize privacy over convenience, or seek devices that offer both?
Start exploring options that align with your lifestyle. Research products that offer local data processing and energy efficiency. Your choices will shape the direction smart homes take in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Smart Edge Computing?
Smart edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and improving performance for IoT devices and real-time applications.
What Is Edge Computing In Simple Words?
Edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and improving speed for real-time applications. It enables faster decision-making.
What Are Examples Of Edge Computing?
Examples of edge computing include autonomous vehicles, smart factories, healthcare IoT devices, content delivery networks, and real-time data processing in retail.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Edge Computing?
Edge computing has limited storage, higher implementation costs, security vulnerabilities, and requires skilled professionals to manage effectively.
Conclusion
Edge computing is shaping smart home systems into faster and smarter solutions. It processes data locally, reducing delays and improving efficiency. This makes devices more reliable for daily tasks. From voice assistants to security systems, the benefits are clear. As technology grows, edge computing will likely play a bigger role.
It offers a glimpse into the future of connected homes. Understanding its impact today can help you prepare for tomorrow. Smart homes are evolving, and edge computing is a key driver. Embracing this technology brings convenience and innovation closer to home.